Why Democracy Faces Challenges in Africa: The Need for Strong Institutions and Civil Society

Africa, a continent rich in diversity and potential, is facing a crisis of faith in democracy. The promise of democratic governance has not translated into prosperity and security for many African nations. Instead, the continent has witnessed political instability, coups, and ongoing conflicts. In this article, we will examine the reasons behind the waning trust in democracy in Africa and explore potential solutions for a more stable and prosperous future.
The Current State of Affairs

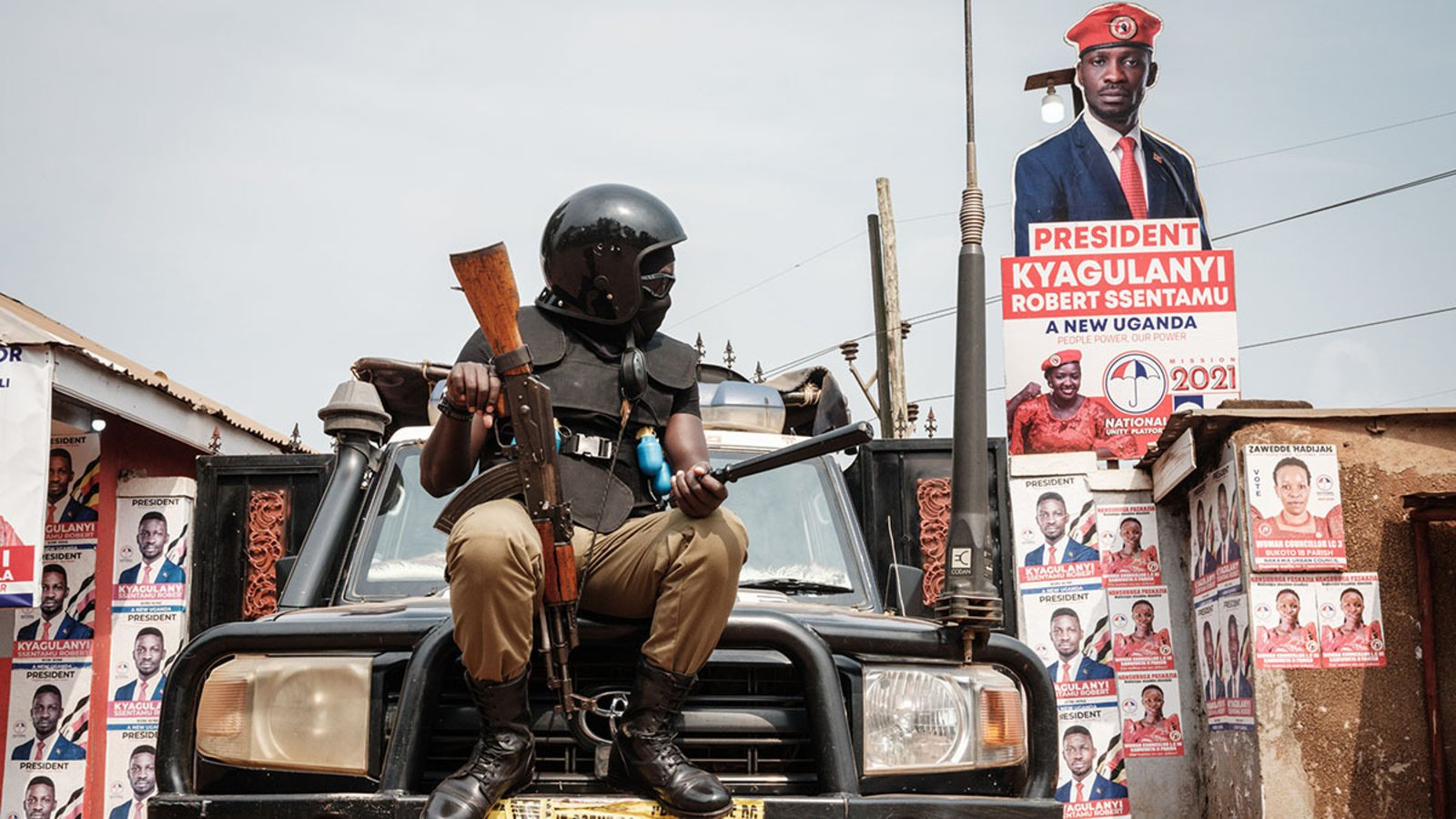
Political Turmoil and Conflict
Africa has been plagued by political turmoil and conflict in recent years. Sudan, for example, has descended into chaos as warlords vie for control, resulting in genocide and widespread violence. Ethiopia has seen one civil war end only to be followed by another. Across the Sahel region, jihadists terrorize communities, and military coups have become alarmingly common. The prevalence of conflict and political instability has eroded trust in democratic systems.
Economic Challenges and Social Discontent
One of the key factors contributing to the loss of faith in democracy is the failure of incumbent regimes to bring about economic prosperity and security. Despite the continent’s vast resources, real GDP per person in sub-Saharan Africa has declined in recent years. Additionally, small-scale conflicts have claimed more lives than ever before, and issues like corruption and inadequate governance persist. As a result, disillusionment and impatience for change have grown among the population.
The Illusion of Democracy

Superficial Democratic Practices
While many African countries have adopted multiparty democratic systems, the reality often falls short of the ideal. In some nations, such as Kenya and Zambia, power transitions occur relatively peacefully through elections. However, in many countries, opposition participation is allowed, but various measures are taken to ensure their inability to secure victory. Manipulation of the electoral process and restrictions on media freedom undermine the legitimacy of these democracies.
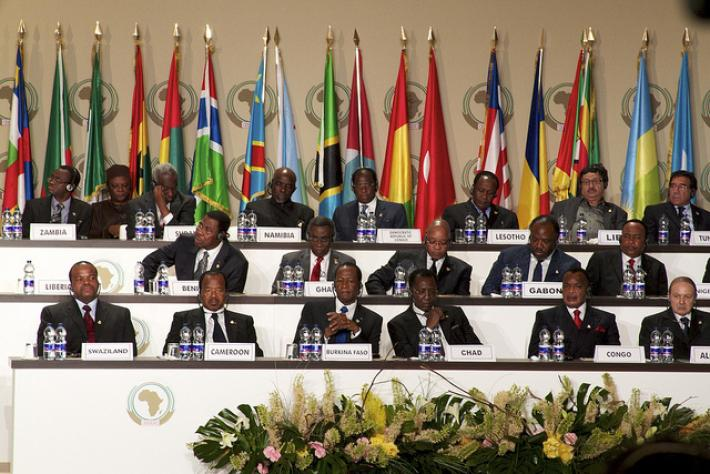
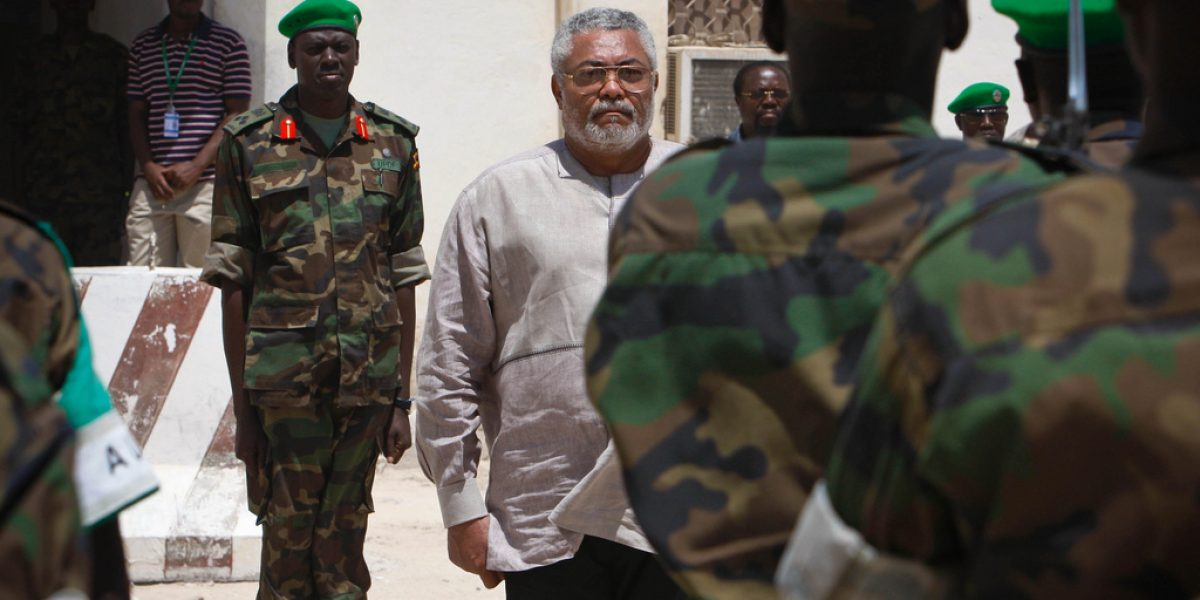
Long-serving Autocrats
Another significant challenge to democracy in Africa is the prevalence of long-serving autocratic leaders. In numerous countries, leaders have remained in power for over two decades, stifling political competition and dissent. This lack of leadership turnover hampers the development of democratic institutions and fosters a culture of entrenched power. The absence of a mechanism to hold government accountable undermines trust in the democratic process.
Geopolitical Shifts and International Influence
Changing Dynamics of International Relations
The global geopolitical landscape has also played a role in the erosion of democracy in Africa. Autocratic regimes have found support from countries like China, Russia, Turkey, and the United Arab Emirates, who are less concerned with democratic principles. These nations are willing to provide financial assistance and arms, creating an alternative power dynamic that undermines Western influence.
Hypocrisy from Western Powers
Western governments, on the other hand, have been inconsistent in their support for democracy in Africa. Instances of turning a blind eye to coups and electoral fraud have weakened their credibility as champions of democratic values. The hypocrisy displayed by these nations undermines the trust of African populations and perpetuates the perception that democracy is merely a façade.
Reversing the Trend: A Way Forward
African-Led Solutions
The primary responsibility for reversing the decline in democracy lies with African nations themselves. The African Union, a regional body, must reassert its commitment to the “no-coup” policy and isolate coup leaders. Additionally, governments claiming to be democratic must prioritize good governance, tackle corruption, and promote inclusive growth. Implementing initiatives like the African Continental Free Trade Area can unlock economic potential and improve livelihoods.
International Support and Collaboration
Rich nations, too, have a role to play in supporting democracy in Africa. They should fulfill promises to provide financial assistance for climate change mitigation and sustainable development. Restructuring unsustainable debts and investing in African economies can help foster stability and growth. Furthermore, the international community can contribute by welcoming African migrants, facilitating educational opportunities, and supporting peacekeeping efforts.
Strengthening Democratic Institutions
To ensure the long-term success of democracy in Africa, it is crucial to strengthen democratic institutions. This includes promoting media freedom, independent judiciaries, and civil society engagement. Building transparent electoral processes and ensuring fair and free elections are also essential. By empowering these institutions, African nations can establish a solid foundation for democratic governance.
Conclusion
The crisis of faith in democracy in Africa is a pressing issue that requires urgent attention. By addressing the underlying causes of disillusionment and implementing comprehensive solutions, African nations can regain trust in democratic systems. Through African-led initiatives, international support, and a focus on strengthening democratic institutions, a more stable and prosperous future can be achieved. It is time for Africa to reclaim the promise of democracy and build a better future for its people.