Today’s Mortgage Rates: Understanding the Current Market Trends
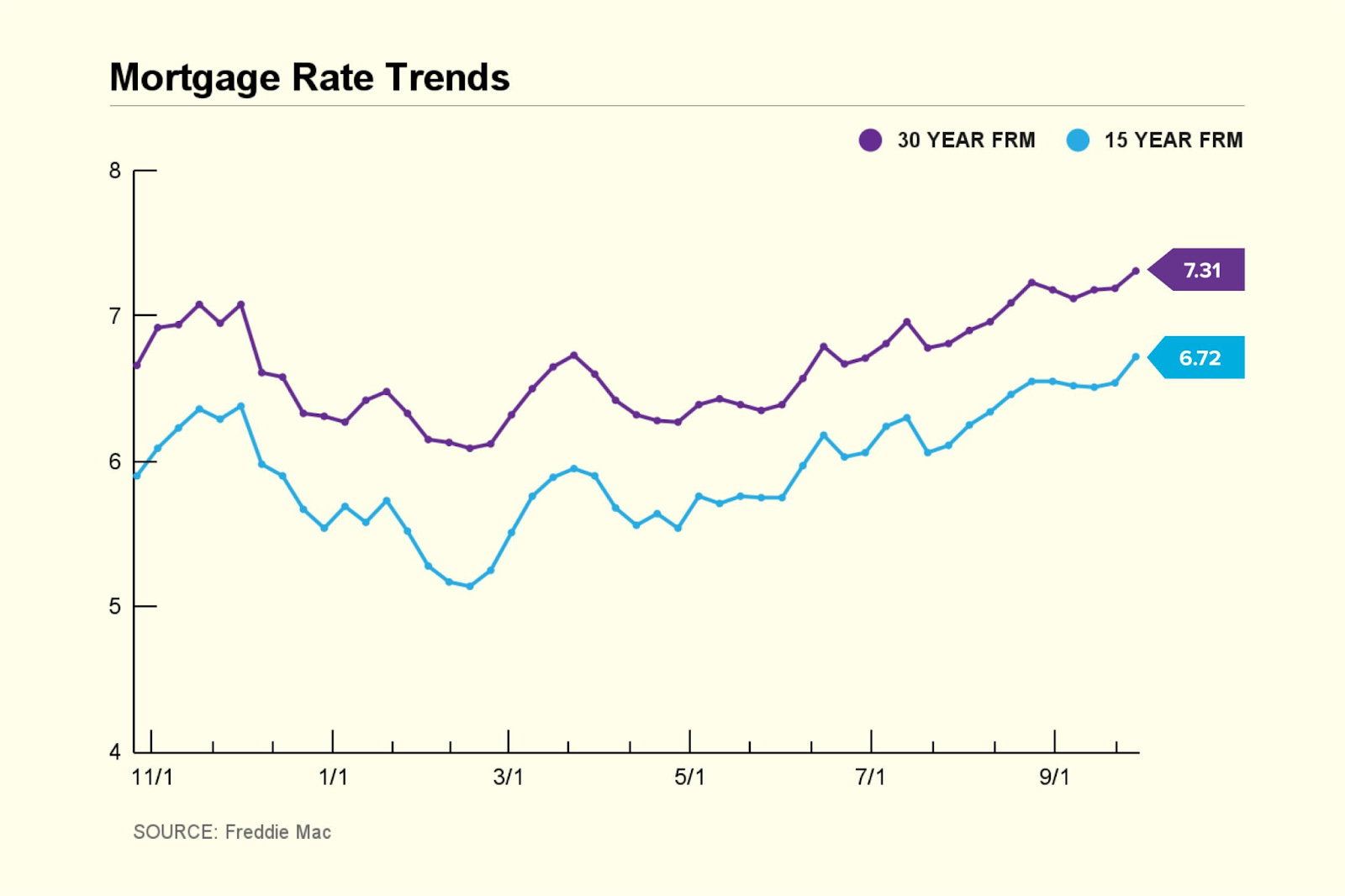
Buying a home is a significant financial decision, and one of the key factors to consider is the mortgage rate. The interest rate on a mortgage loan can determine the overall cost of homeownership and the monthly payments. It’s crucial to stay informed about the current mortgage rates and understand the factors that influence them. In this article, we will explore the latest mortgage rates for 15- and 30-year terms and delve into the key aspects that borrowers should consider when applying for a mortgage.
How Mortgage Rates Work
When you take out a mortgage loan, you’re essentially borrowing money from a lender to purchase a home. The lender charges interest on the principal amount, which determines the cost of borrowing. Mortgage rates are expressed as a percentage and can vary based on several factors, including your credit score, debt-to-income ratio, down payment amount, loan term, and loan amount.
A mortgage can have a fixed or adjustable interest rate. With a fixed-rate mortgage, the interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term. On the other hand, an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) has an interest rate that can fluctuate with the market.
It’s important to note that a mortgage’s interest rate is not the same as its annual percentage rate (APR). The APR includes both the interest rate and any other lender fees or charges.
Factors Influencing Mortgage Rates
Mortgage lenders determine interest rates on a case-by-case basis. They reserve the lowest rates for borrowers with low-risk profiles, including those with higher credit scores, income levels, and down payment amounts. Several personal factors can influence your mortgage rate, including the location and price of the home, your credit score and history, loan term, loan type, interest rate type, down payment amount, loan-to-value (LTV) ratio, and debt-to-income (DTI) ratio.
Economic factors also play a significant role in mortgage rate fluctuations. Factors such as inflation, economic climate, demand and inventory levels in the housing market, current employment rate, and federal reserve policies can impact the average mortgage rates.
To find the best mortgage rates, it’s essential to shop around and compare offers from different lenders. Each lender may have slightly different rates, terms, and fees. Comparing multiple lenders will help you secure the best deal and potentially save thousands of dollars over the life of your loan.
Comparing Mortgage Rates
When comparing mortgage rates, consider the following steps:
- Shop around for lenders: Compare several lenders to find the best rates and lowest fees. Even a small difference in interest rates can result in significant savings over time.
- Get loan estimates: Request loan estimates from multiple lenders. These estimates provide personalized rates and fees based on your financial situation. Review and compare the estimates carefully.
- Get pre-approved: Consider getting pre-approved for a mortgage. Pre-approval gives you a clear understanding of your borrowing capacity and helps you negotiate with sellers.
- Consider rate lock: If you find a favorable rate, you may want to consider locking it in. A rate lock guarantees the current rate for a specified period, protecting you from potential rate increases.
- Choose the right mortgage type: Decide between a fixed-rate mortgage and an adjustable-rate mortgage. Consider your financial goals and risk tolerance when making this decision.
To simplify the process of comparing mortgage rates, online platforms like Credible offer tools that allow you to view rates from multiple lenders without affecting your credit score. Additionally, using a mortgage calculator can help you estimate monthly payments and the total cost of the loan.
Pros and Cons of Mortgages
Before applying for a mortgage, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons. Here are some benefits and drawbacks to consider:
Pros:
- Predictable monthly payments: Fixed-rate mortgages offer consistent monthly payments, providing stability in your budgeting.
- Potentially low interest rates: With a good credit score and a substantial down payment, you may qualify for competitive interest rates.
- Tax benefits: Owning a home can provide tax benefits, such as deductions for mortgage interest and property taxes.
- Potential asset growth: Real estate is often considered a valuable asset that can appreciate over time, potentially increasing your net worth.
- Credit score improvement: Timely mortgage payments can help build and improve your credit score.
Cons:
- Costly fees and interest: Mortgages involve substantial interest payments and fees, increasing the overall cost of homeownership.
- Long-term debt commitment: Mortgages typically span several years, creating a long-term financial obligation.
- Potential rate changes: Adjustable-rate mortgages can lead to fluctuating monthly payments if interest rates increase.
It’s crucial to thoroughly evaluate your financial situation and long-term goals before committing to a mortgage. Consider consulting with a financial advisor to understand the potential impact of a mortgage on your overall financial plan.
Qualifying for a Mortgage
To qualify for a mortgage, you’ll need to meet certain requirements set by lenders. Here are the typical steps to qualify for a mortgage:
- Steady employment and income: Lenders typically require proof of steady employment and income. This may include pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements.
- Review assets: Lenders consider your assets, such as savings and investments, as part of the qualification process.
- Debt-to-income ratio (DTI): Your DTI ratio compares your monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income. A lower DTI ratio increases your chances of loan approval.
- Credit score: Lenders review your credit score to assess your creditworthiness. Higher credit scores generally result in better interest rates and loan terms.
- Property type: The type of property you’re purchasing can impact the loan approval process. Primary residences often have more lenient requirements compared to secondary or investment properties.
- Choose the loan type: Consider different loan types, such as conventional loans, government-backed loans (FHA, VA, USDA), and jumbo loans, to find the best fit for your needs.
- Prepare for upfront and closing costs: Depending on the loan type, you may need to make a down payment and pay closing costs. Prepare your finances accordingly.
Applying for a Mortgage
Once you’re ready to apply for a mortgage, follow these steps:
- Choose a lender: Research and compare lenders to find the best rates, terms, and customer service.
- Get pre-approved: Start the pre-approval process to determine your borrowing capacity and increase your chances of loan approval.
- Submit a formal application: Complete the lender’s application process, providing all required documentation, such as income verification, bank statements, and identification.
- Loan processing: Wait for the lender to process your loan application. They may request additional documentation or clarification during this stage.
- Home appraisal: The lender may conduct a home appraisal to determine the property’s value and ensure it meets lending standards.
- Closing process: If your loan is approved, you’ll receive a closing disclosure with the final loan terms and closing costs. Review the document, pay the closing costs, and sign the necessary paperwork to finalize the loan.
In case of non-approval, consult with your lender to understand the reasons and explore possible solutions. They may provide guidance on improving your credit or addressing any issues affecting your loan application.
Refinancing a Mortgage
Refinancing a mortgage involves replacing your current loan with a new one. The primary reasons for refinancing include obtaining a lower interest rate, adjusting the loan term, reducing monthly payments, removing private mortgage insurance (PMI), or accessing home equity for other financial needs.
The refinancing process is similar to applying for a mortgage. Consider the following steps:
- Determine your goals: Understand why you want to refinance and define your objectives, such as lowering monthly payments or paying off the loan faster.
- Compare lenders: Research and compare lenders to find the best refinancing rates and terms.
- Complete the application process: Provide the necessary documentation and complete the lender’s application process.
- Wait for lender review: The lender will review your application, credit history, and financial documentation to assess your eligibility.
- Complete the home appraisal: The lender may require a home appraisal to evaluate the property’s value.
- Closing process: Review the loan documents, pay any closing costs, and sign the final paperwork to complete the refinancing process.
Refinancing can be a valuable tool to improve your financial situation. However, carefully consider the costs, benefits, and potential impact on your long-term financial goals before proceeding.
Conclusion
Understanding the current mortgage rates and the factors that influence them is crucial for potential homebuyers. By staying informed and comparing offers from multiple lenders, borrowers can secure the best mortgage rates and save thousands of dollars over the life of their loan. Remember to evaluate your financial situation, credit score, and long-term goals before committing to a mortgage. Consult with professionals, such as financial advisors and mortgage experts, for personalized guidance. With proper research and careful consideration, you can make an informed decision and navigate the mortgage market with confidence.